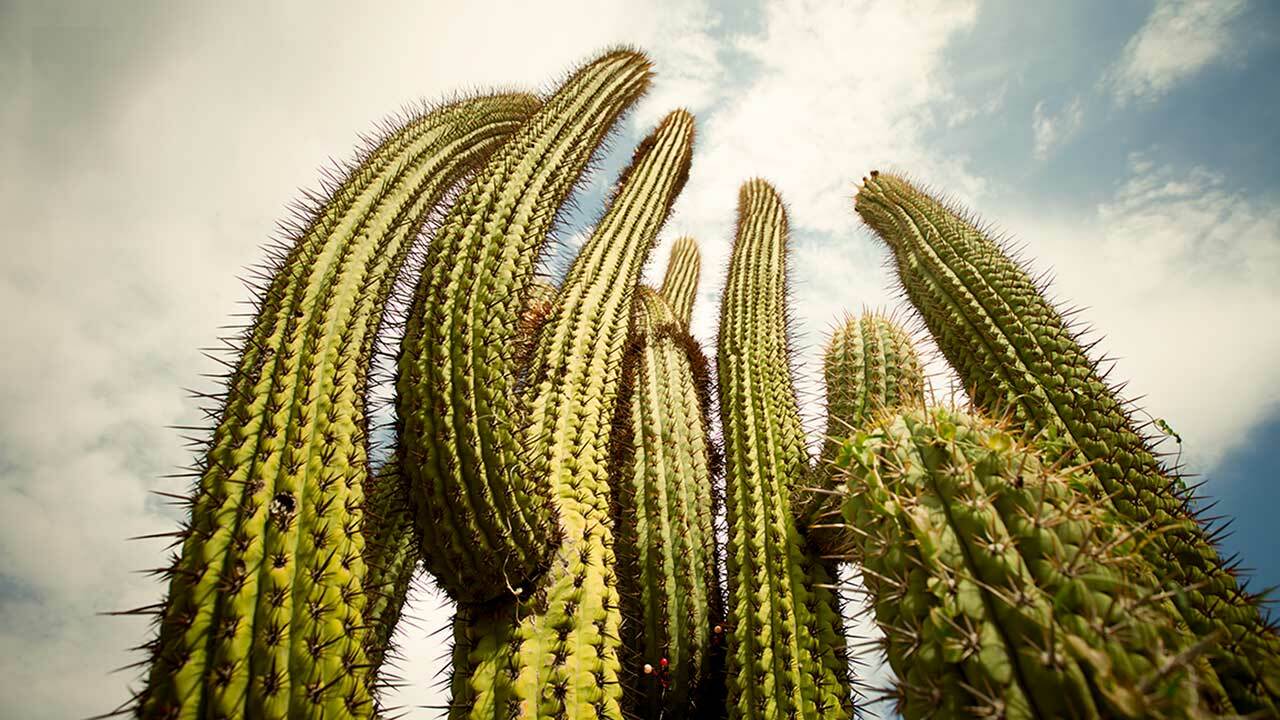
Cacti are a type of plant that is known for its thick, fleshy stem and its spines. These plants are native to the deserts of North and South America, and have adapted to the dry, hot climate by storing water in their stems. Cacti come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes, and they can be found in both arid and semi-arid habitats all over the world.
Cacti’s Unique Design for Water Conservation
One of the most unique things about cacti is their ability to store large amounts of water in their stems. This adaptation helps them to survive in desert conditions where water is scarce. When it rains, cacti absorb water through their roots and store it in their stems. This water is used by the plant during dry periods.
Cacti are able to store such large amounts of water due to their thick, fleshy stems. The stem is covered in a layer of protection that helps prevent evaporation. Cacti also have specialized roots that are able to absorb water quickly.
The shape of a cactus also plays a role in its water-saving abilities. Most cacti have a columnar shape, which means that they have a narrow base and a wide top. This shape allows the plant to minimize its surface area so that less water is lost through evaporation.
Types of Cacti
There are two main types of cacti: opuntias and columnar cacti. Opuntias, also called prickly pears, are cacti that have flat, fleshy pads instead of the traditional cylindrical stem. These plants are covered in spines, and they produce small, edible fruits. Columnar cacti, on the other hand, have a tall, straight stem with ridges running up and down its length. These cacti often grow to be quite large, and are home to many species of animals in their native habitats.
Saguaro Cactus

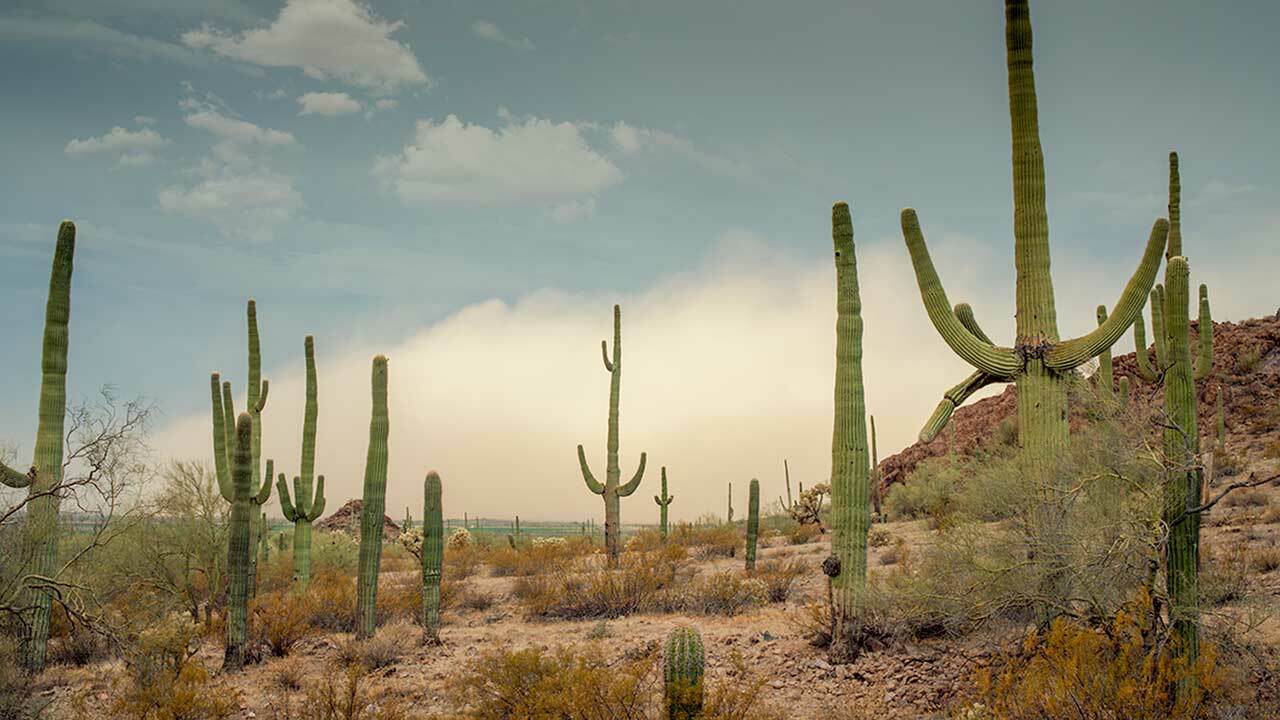
The saguaro cactus is one of the most recognizable types of cacti, and also one of the largest. Saguaros can grow to be over 40 feet tall, and can live for hundreds of years.
Where do Saguaro Cacti grow?
Saguaro cacti are native to the Sonoran Desert, which is located in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. This desert is one of the hottest and driest habitats on earth, and saguaros have adapted to this environment by storing water in their stems.
What do Saguaro Cacti eat?
Saguaro cacti are pollinated by a variety of animals, including bees, birds, and bats. These creatures feed on the nectar that is produced by the flowers of the cactus, and in return, they help to spread the plant's pollen. Saguaros also rely on animals for dispersal; their fruits are eaten by animals such as rodents and javelinas, who then spread the plant's seeds in their droppings.
How do Saguaro Cacti reproduce?
Saguaro cacti reproduce sexually, meaning that they require both a male and female plant to produce offspring. The flowers of the cactus bloom at night, and are pollinated by nocturnal creatures such as bats and moths. Once pollinated, the flowers begin to produce fruits that contain the plant's seeds. These fruits are eaten by animals, who then spread the seeds in their droppings. This method of dispersal ensures that saguaros can colonize new areas as their habitats change.
Did you know?
The saguaro cactus is the official state flower of Arizona. The flowers of the saguaro cactus are large and white.
Prickly Pear Cactus
The prickly pear cactus is another type of cacti native to the deserts of North America. These cacti are smaller than saguaros, and have a more flattened shape. Prickly pears are covered in small, sharp spines, and produce edible fruits that are often used in jams and jellies. The flowers of the prickly pear cactus are large and brightly colored, and bloom in the springtime.
Barrel Cactus
The barrel cactus is a type of cacti that is native to the deserts of the southwestern United States and Mexico. These cacti have a round or cylindrical shape, and can grow to be over 10 feet tall. Barrel cacti are covered in sharp spines, and have large flowers that bloom in the springtime. The fruits of the barrel cactus are edible, and are often used in Native American cuisine.
Support your local PBS station in our mission to inspire, enrich, and educate.
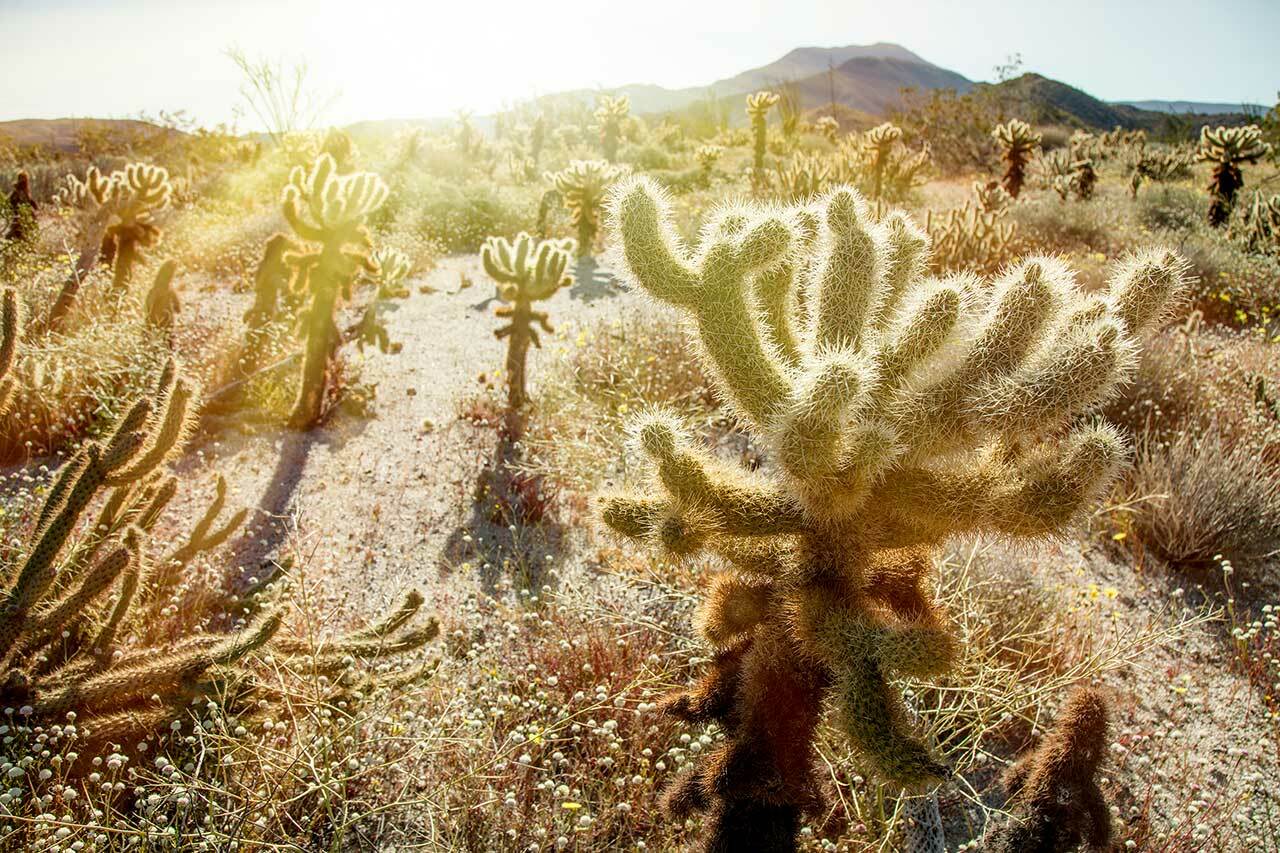

The cholla cactus is a type of cacti that is native to the deserts of the southwestern United States and Mexico. These cacti have a segmented, cylindrical shape, and they are covered in sharp spines. The flowers of the cholla cactus are small and green, and they bloom in the springtime. The fruits of the cholla cactus are edible, and they are often used in Native American cuisine.
Jumping Cholla
The cholla cactus is also known as the "jumping cactus" because its spines are so sharp that they can easily become embedded in the skin. This cactus gets its name from the Spanish word for "thorn," which is "cholla."
Cacti Uses:
Cacti are often used as decoration in homes and gardens, but they can also be used for their medicinal properties. Some cactus species contain compounds that can be used to treat a variety of ailments, including diabetes, arthritis, and headaches.
In addition, cacti can be used as food and water sources in desert habitats. Cactus fruits are often eaten fresh, and the flesh of the cactus can be used to make drinks such as juice and wine. The pads of the cactus can also be cooked and eaten, and are a good source of vitamins and minerals. Cacti are also used in traditional Native American medicine, and are believed to have a variety of healing properties.
Cacti are an essential part of the desert ecosystem. They provide homes and shelter for a wide variety of animals, and their roots help to stabilize the soil. Cacti also play an important role in the water cycle by absorbing and storing water.
Cacti Conservation
Cacti are under threat from a number of different factors, including habitat loss, climate change, and illegal collecting. Habitat loss is the biggest threat to cacti, as their natural habitats are being destroyed by development and agriculture. Climate change is also a major threat to cacti, as it is causing the deserts to become hotter and drier. This changing environment is making it difficult for cacti to survive. Illegal collecting is also a problem, as cacti are often taken from the wild to be sold as houseplants or decoration.There are a number of organizations working to conserve cacti, and their habitats. These organizations are raising awareness about the importance of cacti, and are working to protect and restore cactus populations.
How To Care For a Cactus
While cacti may seem like tough plants that can survive just about anything, they actually require quite a bit of care if you want them to thrive. Here are some secrets to growing healthy cacti:
1. Provide plenty of sunlight. Cacti need direct sunlight in order to grow and produce flowers. If you live in a climate with long, hot summers, your cactus will do best if it's placed in a sunny spot outdoors. If you live in a cooler climate, or if you want to grow your cactus indoors, place it near a south-facing window where it will receive plenty of sunlight.
2. Allow the soil to dry out completely between watering. Cacti are succulents, which means they store water in their stems and leaves. As a result, they don't need to be watered very often. In fact, overwatering is one of the most common mistakes people make when growing cacti. Water your cactus only when the top inch or so of soil is dry to the touch.
3. Don't fertilize too often. Cacti don't need a lot of fertilizer, and too much can actually do more harm than good. If you decide to fertilize your cactus, use a very diluted solution and apply it only once every month or two.
4. Protect your cactus from cold weather. Cacti are native to warm desert climates, so they're not very tolerant of cold weather. If you live in an area that gets frost in the winter, it's best to grow your cactus indoors where it will be protected from the cold.
5. Be careful when handling cacti. The spines on some cacti can be quite sharp, so it's important to handle them with care. If you need to move your cactus, or if you want to repot it, be sure to wear gloves to protect your hands.
Cacti Fun Facts
Cacti are one of the most recognizable plants in the world, but there are still many people who don’t know much about them. Here are a few fun facts about these fascinating plants:
• Cacti are not just found in the desert. There are actually around 1,500 different species of cactus, and can be found all over the world, from the coldest mountains to the hottest rainforests.
• The largest cactus in the United States is the saguaro, which can grow to be over 60 feet tall!
• Cacti come in all sorts of shapes and sizes. Some are small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, while others can grow to be as large as a house.
• Cacti store water in their stems, which is why they are often used as an icon of the desert.
• The spines on cacti are actually modified leaves. They help to protect the plant from animals and reduce water loss by shading the stem.
• Many species of cactus are endangered due to habitat loss and human development.
This article was researched and compiled by Sandler Digital in collaboration with PBS.