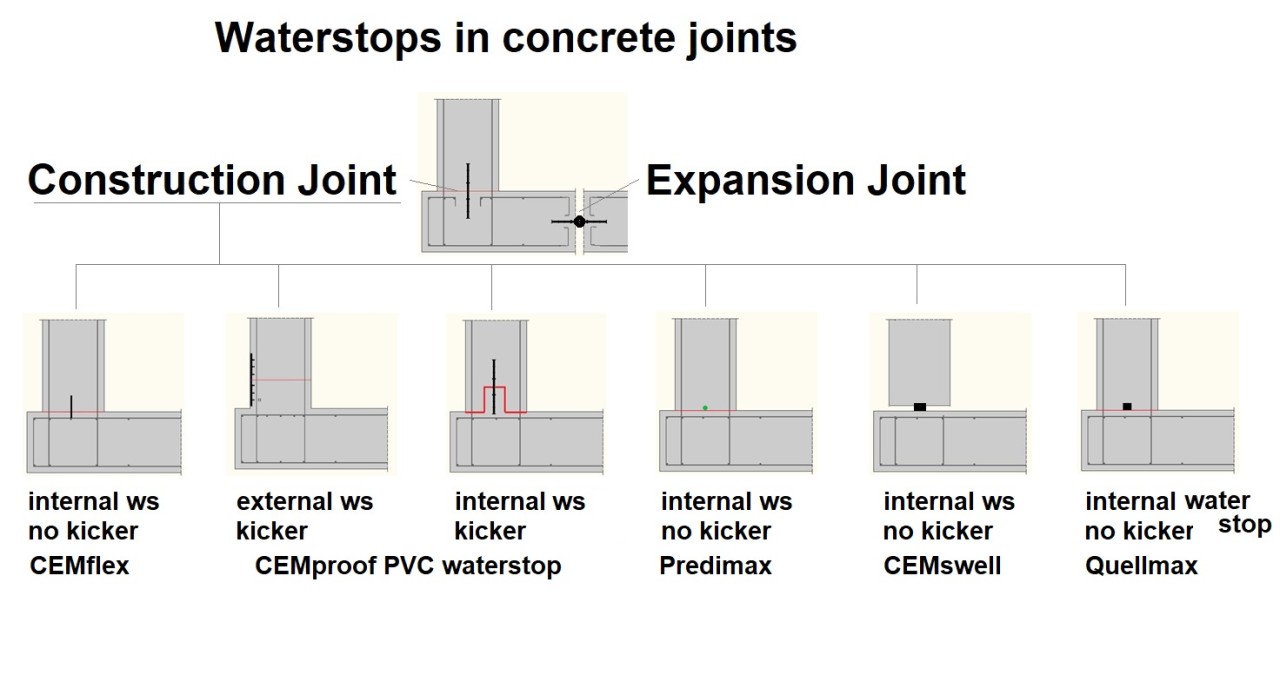
Waterstops in concrete joints
Waterstops or waterbars are premanufactured joint filler / concrete joint sealing systems used to prevent the transmission of liquids and water through the concrete construction joint. Waterstops are mainly used for the waterproofing of below-grade concrete structures like tunnels, cut and cover tunnels, water treatment facilities, storage and filling facilities for manure, slurry and silage effluent and biogas storage and liquid tight filling facilities, parking structures, water reservoirs, sewage treatment facilities, and marine structures.
The basic features (waterproofing) and advanced features (drinking water approval, chemical resistant and biogas resistant) and types of waterstops used in construction are explained briefly in this article.
Waterstops for Concrete Construction Joint
Waterstops are highly demanded in locations where the construction joints are common:
- The transition area between the horizontal and vertical concrete components.
- Long length wall areas, where two or more formwork is required for casting
- Situations when concrete placement is paused or stopped for some reason (cold joint)
- Where a change in design form is required for the design elements.
The construction joint is also referred to as cold joints which occur when the before placed concrete cures earlier than the adjacent one. These are the most likely areas which can result in water ingress. In most of the cases, the construction joint is not actually formed. But, a construction joint, like the control joint is introduced in order to facilitate the shrinkage caused due to large displacements.
Note: Cold joints needs to be avoided! The waterproofing desing must be done in an early design stage in combination with the architect, structural-engeneer, civil-engineer, hydrologist/geologist and design-engineer. The result of a proper waterproofing desing and a good on-site quality is to avoid "cold joints" completely.
A cold joint is a plane of weakness in concrete caused by an interruption or delay in the concreting operations. It occurs when the first batch of concrete has begun to set before the next batch is added, so that the two batches do not intermix. Sometimes cold joints occur because of emergency interruptions and delays and sometimes because of the work stoppage at the end of the day, but they can 'also occur from poor consolidation. To prevent cold joints in walls, beams and other structural components it is necessary to place concrete in layers and intermix each layer with the previous one by using a vibrator. A cold joint is a result of bad workmanship, bad design, bad on-site supervision and / or bad organization on site. A cold joint need to be avoided!
Is waterproofing required?
Most of the below-grade concrete structures have conditions that result in the infiltration of the water into the construction joints. To prevent such leakage, waterstops are introduced into the construction joint. Waterstops have proven best for such infiltration issues observed in the construction joint.
Structural Waterproofing design - has to be done individually according to site conditions
A waterstop installed in concrete joints is an important component of the overall waterproofing design. Use of a waterstop with a waterproofing membrane is considered a belt-and-suspenders approach to provide a dry basement. This is a common practice in waterproofing design because if for some reason water is able to circumvent the membrane, the waterstop is in position to obstruct the water in the most likely place the water leak can occur – through the concrete cold joint. Beyond the concrete cold joint, waterstops are unable to prevent water ingress through cracks that develop in the concrete due to building settlement, load deflection, or concrete shrinkage - pre-applied waterproofing membrane systems, are available for these crack issues.
Waterstops are premanufactured joint fillers that come in numerous sizes, shapes, and types. The most widely used waterstops from 1920s are made out of steel / metal sheet plate waterstop (black steel). In the 1950s the next generation of waterstops were made from PVC. PVC waterstops are flexible and relatively strong. New materials like hydrophilic rubber, bentonite waterstops, injection hoses systems followed in the 1980s.
The waterstops are available in the following compositions:
- Steel plate waterstop / metal waterstop e.g., 2mm thick, 30 cm high metal waterstop
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) waterstop e.g., CEMproof PVC waterstop
- Thermoplastic Rubber based waterstop e.g., PVC/Elastomeric
- Hydrophilic Rubber based waterstop e.g., CEMswell hydrophilic rubber
- Bentonite Clay based expanding waterstop e.g., Quellmax bentonite waterstop
- Injection hose systems with various injection material e.g., Predimax injection hose
- Special coated steel plate waterstop e.g., CEMflex
Types of Waterstops mostly used today!
The 4 major types of waterstops are actively used today:
- Thermoplastic Waterstop / PVC Waterstops – mostly internally expansion joints
- Hydrophilic Waterstop / Bentonite Waterstops – mostly internally construction joints
- Injection hose systems – mostly additionally to other systems in tunnels und underground structures
- Metallic Waterstops with special coating
A PVC waterstop is installed either externally or better internally. The function of a PVC waterstop is to stop the waterflow trough the concrete construction joints, the PVC waterstop creates a tough physical barrier. Based on the type of construction joint, the width, size and thickness of the waterstop varies.
A PVC waterstop must be installed by skilled installers using welding equipment to seal / weld the overlapping and connecting areas. I am recommending a thermoplastic waterstop for internal use - mostly to seal expanion joints (for construction joints we do have much more suitable systems available).
Hydrophilic rubber waterstops also comes under the hydrophilic / swelling waterstop category. This material also swells and forms a compression seal in the construction joints in the concrete structure. An increase of 800% is expected by this type.
Hydrophilic waterstops can be either applied in the form of strips or by means of a caulking gun, which makes the installation process easy. CEM805 active out of cartridge or soft sausage. This material requires 24 hours for curing, only after which concrete pouring is expected to perform. So, throughout the curing process of the concrete, the urethane material must remain dry. Long exposure of waterstops to water results in its wear out. I recommend hydrophilic rubber for prefabricated concrete elements and for detailing such as pipe penetrations (caulking gun).
Bentonite waterstop is a type coming under the hydrophilic waterstop category. Bentonite, as we know is a swellable clay (montmorillonite) compound. It has the property to expand up to twelve times when it comes in contact with the water. This filling property is used to seal in-situ concrete construction joints. This waterstop actually compression seal the system thus filling the cracks and the voids in the concrete. One of the challenges in installing this system is that the bentonite must be maintained dry until it is poured into the joint which has to be sealed. Premature exposure of the bentonite to moisture results in the damage of the joints and weakening of the concrete around the joint. This is the reason why I recommend to use bentonite waterstop tapes with an effective rain-protection coating.
Injection-hose systems / injection-tube waterstops are usually a permeable or perforated hose installed during new construction with a series of injection ports and valves. These ports are placed exposed at the interior surface of the concrete for later access. Should a leak occur after construction, a grout pump can be used to inject a resin (usually polyurethane) to seal the joint and fill any concrete cracks / honeycombs and/or adjacent voids in the concrete. Each injection hose system uses permeable or perforated hose that is installed at construction joints, in short lengths (typically less than 40 ft.). I recommend to use injection hose systems with a smooth surface due to the fact that the injection material can be injected into the concrete joint with low pressure.
Modern Metallic waterstops are mostly made from steel (carrier), galvanized steel, stainless steel with additional special coating. If we talk about metallic waterstop we talk about the new generation of metallic waterstop with special coatings to support the positive sealing effect. These metal waterstops are embedded internally in the concrete construction joint. These are very strong and can be exposed to extreme temperature conditions and chemical atmosphere. This is hence highly applied in the construction of dams and heavy construction projects such as tunnels, cut and cover tunnels and deep basements.
Contractors have the most important role with regards to structural waterproofing as well as waterstops. NOTE: Structural waterproofing desing has to be done in an early design stage.
The installation. Waterstops should be treated as strategic building envelope barrier material for the long-term success of a project. On site supervision by a waterproofing engineer / spezialist is very important to pay attention on a proper installatio. A on site quality plan has to be followed.
For any waterstop to be effective, proper design, installation, and concreting practices must be followed. Most importantly, one must select a product size and profile suitable for the expected joint movement (only internal expansion joint waterstop), hydrostatic head, and chemical resistance required.
How does a proper waterproofing design look like? It is mostly a combination between Type A and Type B waterproofing.
Adrian Pflieger, civil-engineer and expert in the field of structural waterproofing

















PhD student in Civil Engineering| Interested in promoting engineering awareness
7moThank you so much for this very informative post Dipl.-Ing., Dipl.-Wirt.-Ing. Adrian Pflieger Is the decision to use a waterstop a matter for engineers and contractors to determine, or is it a mandatory requirement? Do we have codes to define its use; whether in types, thickness and so on terms?
Ingeniero Civil
2yCould you said me? What is the relationship between the thickness of the wall or slab and the width of the waterstop with central bulbous?